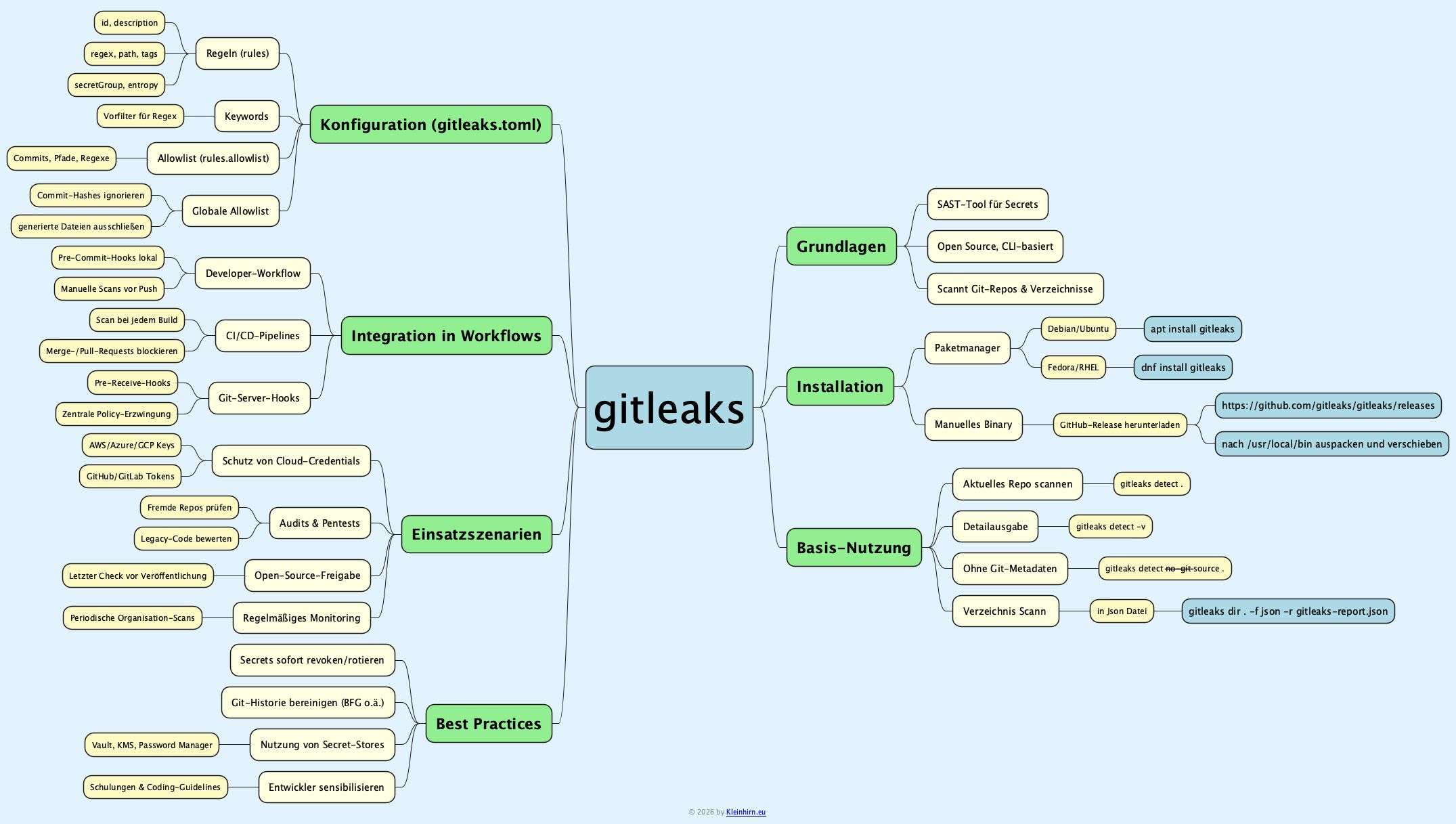
Gitleaks ist ein Open-Source-Tool, mit dem sich hartkodierte Secrets wie Passwörter, API-Keys oder Tokens in Git-Repositories und beliebigen Verzeichnissen unter Linux (ua.) automatisiert aufspüren lassen. Durch seine konfigurierbaren Regeln und die Integration in lokale Workflows oder CI/CD-Pipelines eignet es sich sowohl für Pentester als auch für Entwicklungsteams, die ihre Codebasis systematisch auf Leaks prüfen wollen.
Einordnung und Sicherheitskontext
-Gitleaks gehört zur Klasse der SAST-Werkzeuge, die Quellcode statisch auf verräterische Muster wie Schlüssel, Tokens oder Zugangsdaten durchsuchen.
-Das Tool unterstützt inzwischen über 160 Secret-Typen und kombiniert reguläre Ausdrücke mit Entropie-Heuristiken, um Zufallsstrings mit hoher Aussagekraft zu erkennen.
-Typische Einsatzszenarien sind Security-Audits, Pentests von fremden Repositories sowie das Absichern der eigenen Git-Historie inklusive älterer Commits vor versehentlich eingecheckten Geheimnissen.
Installation unter Linux
Unter Debian/Ubuntu und anderen gängigen Distributionen lässt sich Gitleaks direkt über den Paketmanager installieren. Alternativ kann das aktuelle Release als Binary von GitHub bezogen werden.
Installation auf einem Rapberry Pi ist schnell gemacht:
Debian/Ubuntu und Derivate:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install gitleaks
Die Version ist aber nicht so aktuell, deshalb besser das aktuelle Binary laden und installieren:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
# Version laden wget https://github.com/gitleaks/gitleaks/releases/download/v8.30.0/gitleaks_8.30.0_linux_armv7.tar.gz # Auspacken und installieren sudo tar xf gitleaks_8.30.0_linux_armv7.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin gitleaks # Version checken gitleaks version # Ergebnis 8.30.0 |
Dann mal der 1. Scann, in meinem Home Verzeichnis. Das Ergebeniss soll in eine Datei im Json-Format geschrieben werden:
gitleaks dir . -f json -r gitleaks-report.json
Nach ein paar Minuten kann das Ergebnis auf der Konsole ausgegeben werden:
cat gitleaks-report.json
Oder nur die Beschreibung und der Fundort mit jq:
jq -r ‚.[] | „\(.File) ——> \(.Description)“‚ gitleaks-report.json
Liefert bei mir (fake) ua.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
.zsh_history ------> Identified a Vault Service Token, potentially compromising infrastructure security and access to sensitive credentials. .zsh_history ------> Identified a Vault Service Token, potentially compromising infrastructure security and access to sensitive credentials. .zsh_history ------> Discovered a potential authorization token provided in a curl command header, which could compromise the curl accessed resource. .zsh_history ------> Detected a Generic API Key, potentially exposing access to various services and sensitive operations. history.txt ------> Identified a Vault Service Token, potentially compromising infrastructure security and access to sensitive credentials. history.txt ------> Discovered a potential authorization token provided in a curl command header, which could compromise the curl accessed resource. history.txt ------> Detected a Generic API Key, potentially exposing access to various services and sensitive operations. |
Weitere Infos unter: gitleaks -v oder hier.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
Gitleaks scans code, past or present, for secrets Usage: gitleaks [command] Available Commands: completion Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell dir scan directories or files for secrets git scan git repositories for secrets help Help about any command stdin detect secrets from stdin version display gitleaks version Flags: -b, --baseline-path string path to baseline with issues that can be ignored -c, --config string config file path order of precedence: 1. --config/-c 2. env var GITLEAKS_CONFIG 3. env var GITLEAKS_CONFIG_TOML with the file content 4. (target path)/.gitleaks.toml If none of the four options are used, then gitleaks will use the default config --diagnostics string enable diagnostics (http OR comma-separated list: cpu,mem,trace). cpu=CPU prof, mem=memory prof, trace=exec tracing, http=serve via net/http/pprof --diagnostics-dir string directory to store diagnostics output files when not using http mode (defaults to current directory) --enable-rule strings only enable specific rules by id --exit-code int exit code when leaks have been encountered (default 1) -i, --gitleaks-ignore-path string path to .gitleaksignore file or folder containing one (default ".") -h, --help help for gitleaks --ignore-gitleaks-allow ignore gitleaks:allow comments -l, --log-level string log level (trace, debug, info, warn, error, fatal) (default "info") --max-archive-depth int allow scanning into nested archives up to this depth (default "0", no archive traversal is done) --max-decode-depth int allow recursive decoding up to this depth (default 5) --max-target-megabytes int files larger than this will be skipped --no-banner suppress banner --no-color turn off color for verbose output --redact uint[=100] redact secrets from logs and stdout. To redact only parts of the secret just apply a percent value from 0..100. For example --redact=20 (default 100%) -f, --report-format string output format (json, csv, junit, sarif, template) -r, --report-path string report file (use "-" for stdout) --report-template string template file used to generate the report (implies --report-format=template) --timeout int set a timeout for gitleaks commands in seconds (default "0", no timeout is set) -v, --verbose show verbose output from scan --version version for gitleaks Use "gitleaks [command] --help" for more information about a command. |
Download gitleaks.pdf.
